
This notes is for the course Kuberenetes for absolute beginners
Container orchestration
Kubernetes is a Container Orchestration technology. Docker has its own container orchestration - docker swarm. There is also MESOS from Apache.
The process of automatically deploying and managing containers (scaling up when load increases and scaling down when load decreases) is known as Container Orchestration.
Advantages of container orchestration
- Application is highly available, since there are multiple instances of the application running on different nodes.
- User traffic is load balanced across various containers. When demand increases, deploy more instances of the application seamlessly this can be done at the service level.
- When we run out of hardware, we can scale the number of nodes up/down without having to take down the application.
- All of the above can be done with a set of declarative object configuration files.
Kubernetes components
Nodes
Node is a machine (physical or virtual) on which k8s is installed. A node is worker machine and this is going to hold the containers launched by kubernetes.
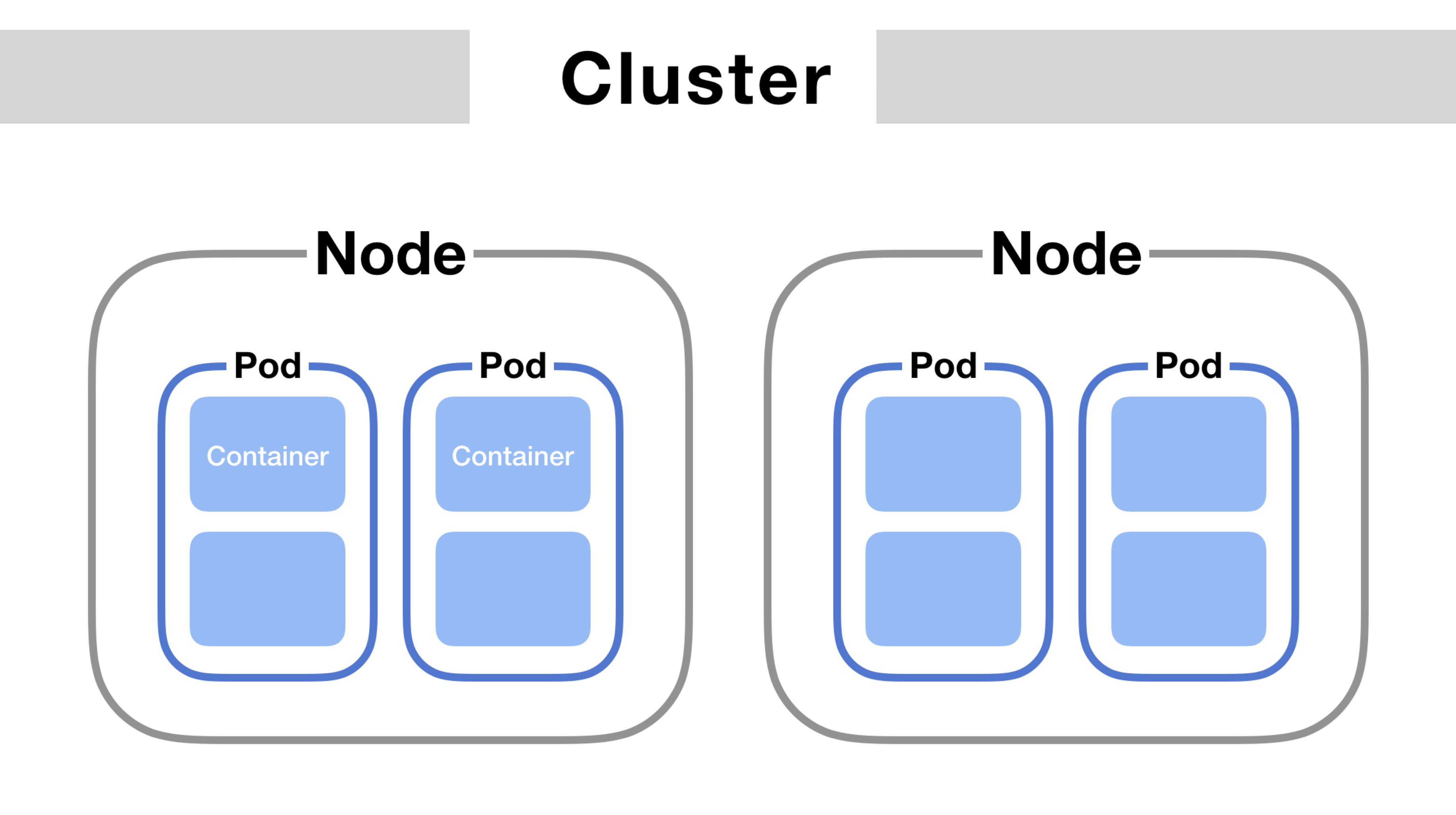
Cluster
Cluster is a set of nodes grouped together. This way, even if one node fails, the application is still accessible from other nodes.
Multiple nodes would help with sharing load as well.
Master
Master is another node with kubernetes installed in it and is configured as a master. The master watches over the nodes in the cluster and is responsible for the actual orchestraction of containers on the worker nodes.
Few responsibilities of master node
- Responsible for managing the cluster.
- Stores the information about the members of the cluster.
- Monitor nodes.
- Moving the workload of the failed nodes to another worker nodes.
Components of Kubernetes (Control plane)
When a k8s is installed on a system, the following components are also installed
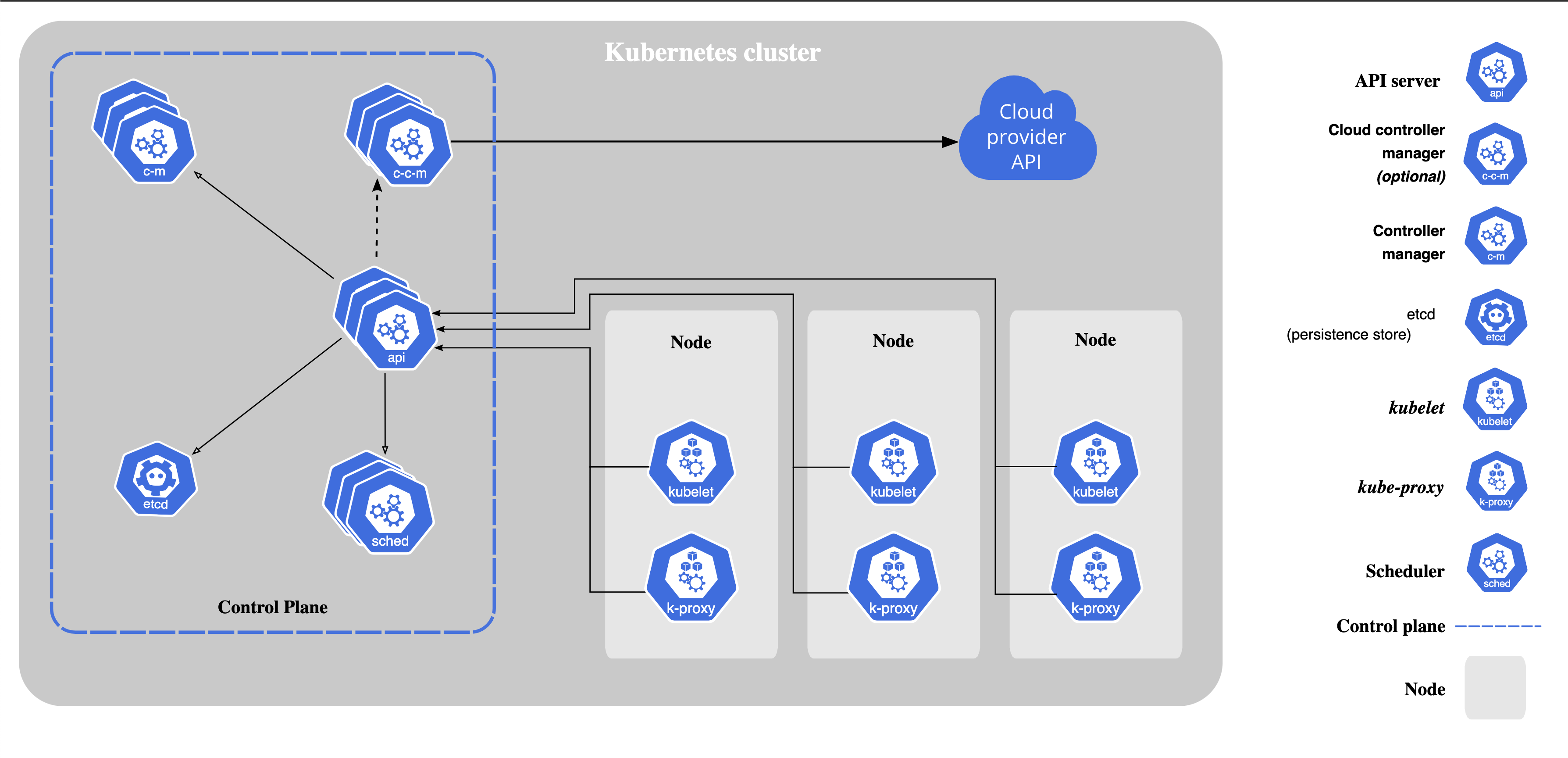
1) An API server - An API server acts as a front-end for kubernetes. The users, management devices, CLI all talk to the API server to interact with kubernetes.
2) An ETCD service - It is a reliable key-value store to store all the data used to manage the cluster. ETCD stores the information of multiple nodes and multiple masters in the k8s cluster in a distributed manner. ETCD is also responsible for implementing locks within the cluster to ensure there are no conflicts between the masters.
3) A Kubelet service - It is an agent that runs on each node in the cluster. It is responsible for making sure that containers are running on the nodes as expected.
4) A Container runtime - An underlying software that is used to run the containers. (Docker)
5) Controllers - They are the brain behind the orchestration. They notice and respond when the nodes, containers or endpoints go down. The controllers would make decisions to bring up new containers in such case.
6) Schedulers - Responsible for distributing work or containers across multiple nodes. It looks for newly created containers and assigns them to Nodes.
The following factors are taken into account for scheduling decisions
- Individual and collective resource requirements
- Hardware/software/policy constraints
- Affinity and anti-affinity specifications
- Data locality
- Inter-workload interference
- deadlines
Master vs Nodes
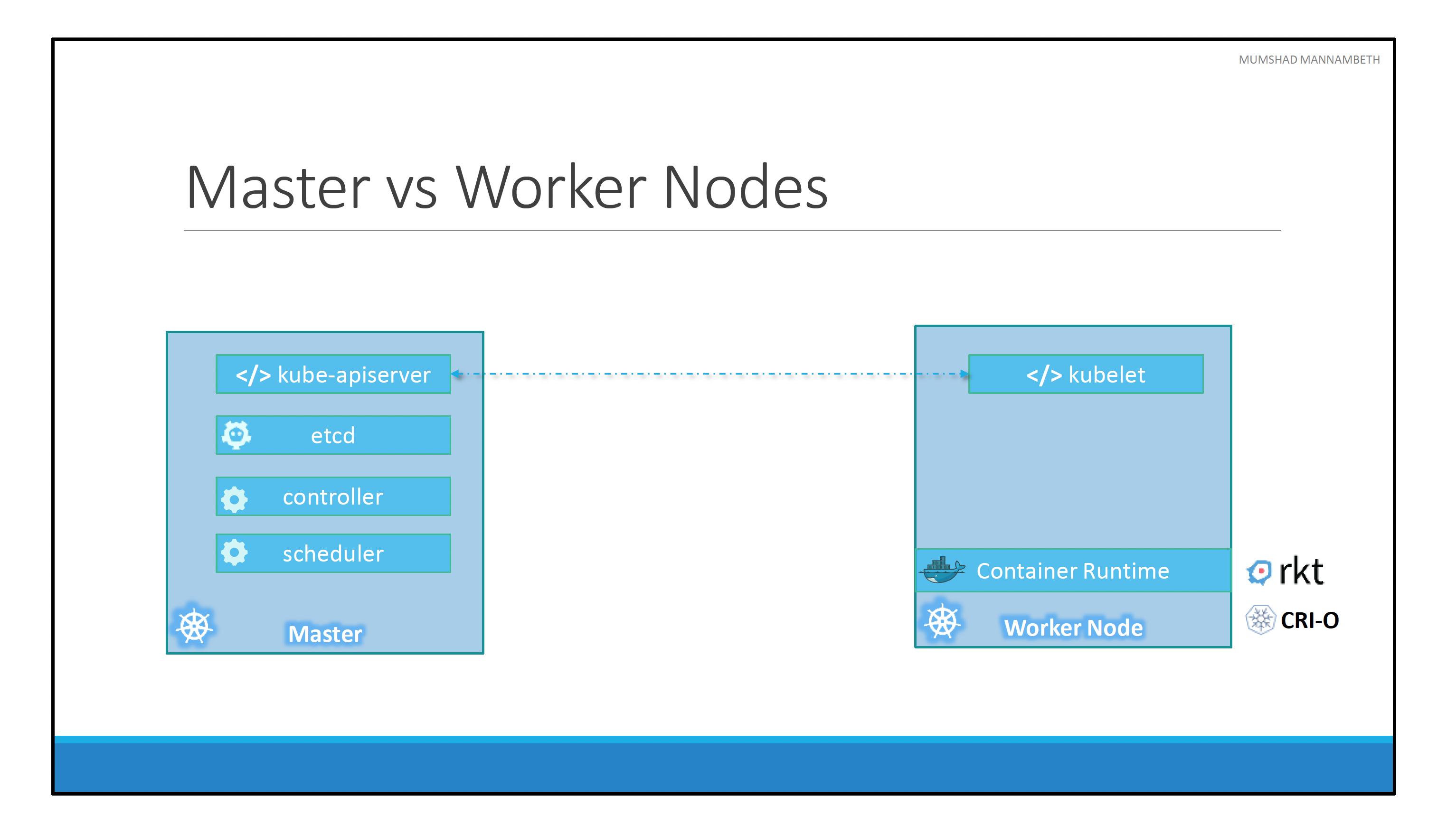
The master node has
- Kube-apiserver installed
- ETCD
- Control manager
- Scheduler and more.
Worker node has
- Container run time installed.
- Kubelet agent - provides health information of the worker node to the master and carry out the actions requested by the master on the worker nodes.
Kubectl (kube control)
Tool used to deploy and manage applications on a Kubernetes cluster
- Provide cluster information
- Get status of nodes in the cluster
Pod
Kubernetes does not deploy containers directly on the worker nodes. The containers are encapsulated into a kubernetes objects known as pods. A Pod is a single instance of an application and is the smallest object that can be created in kubernetes.
To scale up an application, we create a new pod instead of creating additional container inside of an existing pod. A pod can hold additional containers as well (usually not of the same kind). The additional container can be a helper container that supports the main application. The two containers can communicate with each other directly by referring to each other as localhost since they share the same network namespace. They share the same storage space as well.