
This notes is for the course Kuberenetes for absolute beginners
Introduction
Container orchestration system = Container + Orchestration
What are containers
- Containers have their own processes, network and mounts
- Multiple containers can share the underlying operating system kernel.
Docker (most popular container technology).
Problems before containers
- Application component and services being incompatible with underlying OS.
- Compatibility between services, libraries and dependencies on the OS.
- Compatibility checks had to be make during every component upgrade AKA matrix from hell.
- On-boarding a new developer / setting up a local instance was difficult.
With docker
- Each component can run in its own container with its own libraries and dependencies.
- Docker is compatible with any operating systems.
- On-boarding a new developer / setting up a local instance is very easy.
Os components and responsibilities
All operating systems consists of two important components
- OS Kernel
- Software
Os kernel is responsible for interacting with underlying hardware. Custom software differentiates operating systems from each other. Docker container shares the underlying kernel of docker host. Docker is not meant to virtualise and run different operating systems on the same hardware. The main purpose is to containerize and ship them.
Docker vs Virtual machines
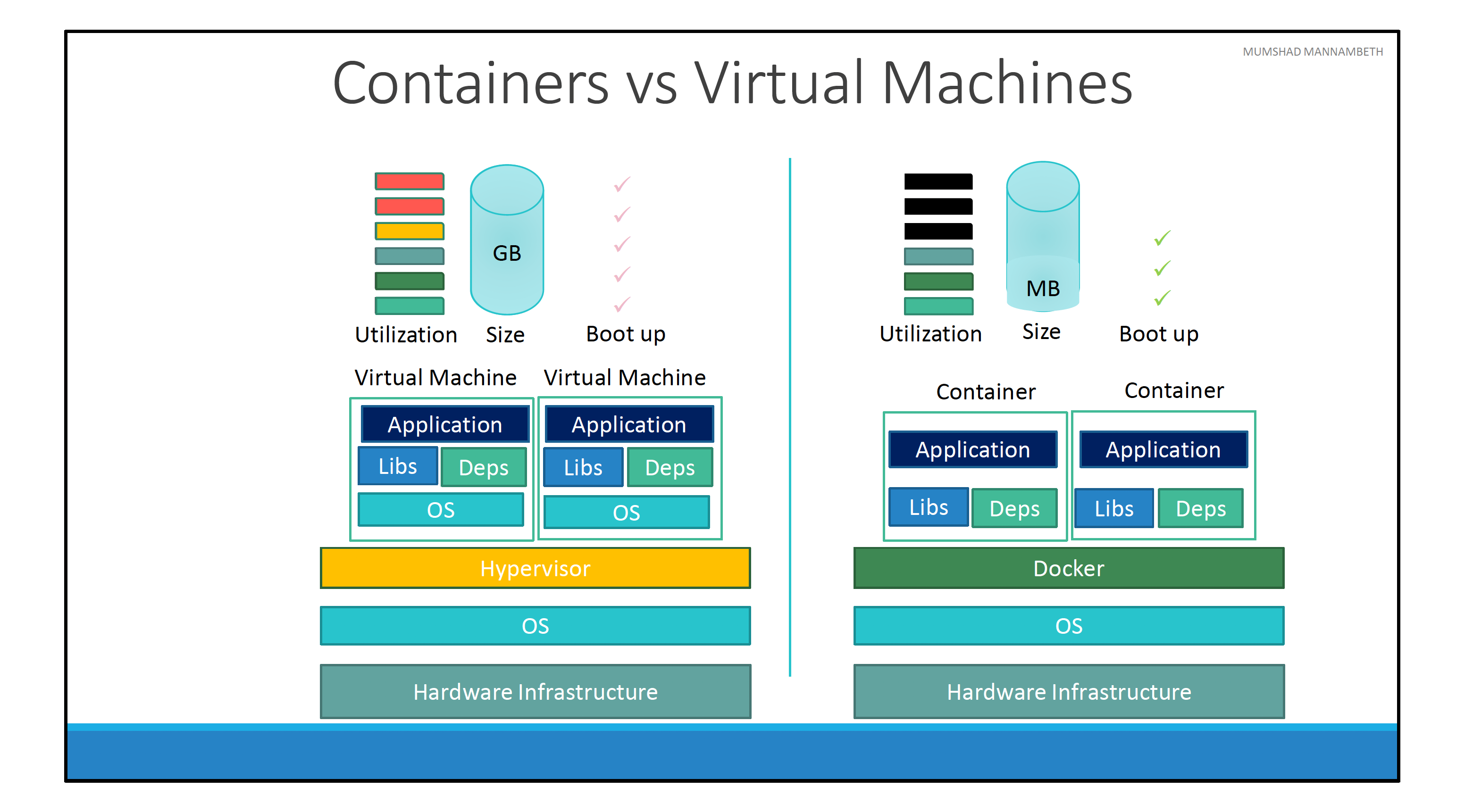
In case of docker we have
- Underlying hardware infrastructure.
- Operating system
- Docker installed on the OS (which is responsible for managing the containers that run with libraries and dependencies).
In case of virtual machine
- Underlying hardware infrastructure
- Operating system
- Hypervisor (ESX or virtualization)
- Virtual machine
- Virtual machine has its own OS inside
- Dependencies
- Application
The overhead causes higher utilization of underlying resources because there are multiple operating systems and kernel running. The Virtual machine is heavy and consume high disk space (Gigabytes) whereas Docker containers a re light weight and are usually mega bytes in size.
Docker containers boot up faster (within seconds). VM takes minutes to boot up as it needs to boot up the entire OS.
Docker has less isolation as more resources (like kernel) are shared between containers.
For VMs, there is complete isolation. Since VM does not directly rely on underlying OS or kernel, we can run different OS such as linux / windows based on same hypervisor.
Reference : https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/hypervisor.html?resource=cat-1023790256#cat-1023790256
Image vs Containers
An image is a package or a template that is used to create one or more containers.
Containers are running instances of that image that are isolated and have their own environments and set of processes.
Advantage of containers
Traditionally, developers developed applications and hand it over to Ops team to deploy and manage it in production environments along with some instructions. If they hit an issue, they would have to work with developers to resolve it.
With docker, major portion of this infrastructure setup is now in the hands of developers in form of Docker file. The instructions that were put together previously (handed off to the ops team) can now put together easily into a Docker file (to create an image for their application). The image can run on any container platform and is guaranteed to run the same way everywhere. Ops team can now use the image to deploy the application. Since OPS team are not modifying it, it continues to work the same when deployed in production.